It happens to the best marketers. You search for your website on Google and notice the search engine has indexed some pages that you would have preferred to keep private or hidden. This could include outdated information, duplicate content or content that contains sensitive or private information.
Once you’ve discovered this content on Google, one of your first reactions may be to panic.
Take a breath! And remember the following options for getting content removed from Google’s cache:
1) Remove or update the content
Before applying a no-index tag, decide what kind of content you are dealing with:
- If the content in question is of a private nature, remove the content from your site or ensure security is enabled on the page so that crawlers are not able to access password-protected content. If removing the content completely, be sure to set up a 301 redirect so users can be sent to a relevant page instead of being met with a 404 error page.
- If the content only needs to be updated, make your changes in your CMS and then allow Google to re-index quickly by entering the URL into Google Search Console.
- If it’s duplicate content (for example, any blocks of content that appear more than once across the site) that should remain on your website, keep the content as is and then apply a no-index tag to the pages you do not want indexed. In addition, implement a rel=canonical link reference to the page you DO want indexed.
At this point, you can wait for Google to re-crawl your website and the content should drop out of search results or be updated automatically.
But, if the content issue is urgent and you would like it to be removed right away, proceed to Step 2.
2) Add the URL to the “Removals” tool in Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool offered to anyone that manages or owns a website.
If you are not already a verified owner of the website, follow verification instructions provided by Google then:
- Log in to your account
- Choose “Removal” from the “Index” menu
- Select the “Temporary Removals” tab
- Hit the “New Request” button (keep it on “Remove this URL only”) and enter the URL of the page you wish to remove entirely from search results and Google’s cache
- Then click “Submit Request”
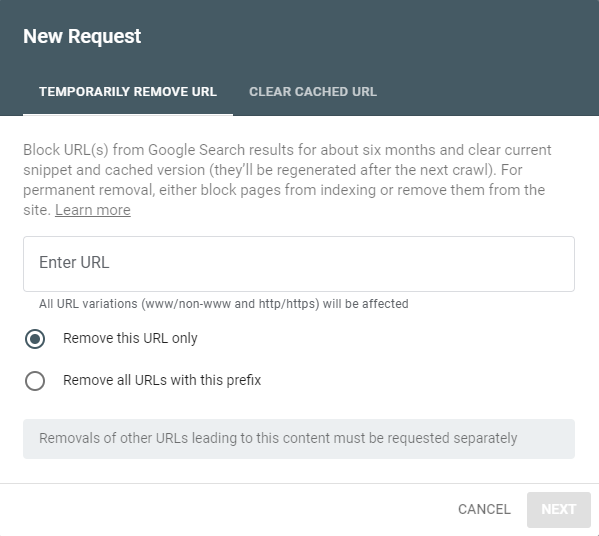
Google will typically process your request within 24-48 hours.
Other options in this section:
- If you’d like the URL to remain but you want the cache and snippet for the page to be updated faster:
- Select the “Clear Cached URL” tab
- If you’d like to remove an entire folder or directory of your site from search results:
- Select “Remove all URLs with this prefix”
You’ll know when your request has been processed once a “Removed” status appears on your Submitted Requests list. Please note this is only a temporary fix. To permanently remove the content you need to remove it from your site or update the source page.
PRO TIP:
If you are looking to ensure your content is being removed as quickly as possible, Google offers an additional tool to remove outdated pages, it is a part of Search Console; but is accessed through the Public Search Console Help page. For this application, you do not have to be a verified owner of the website. When you enter the URL you wish to delete, the tool will then analyze the URL to determine whether the content was removed. If it has, it will process your request as an Outdated Page Removal. The immediate detection is protection from unauthorized page removal requests.
3) Check search results to determine if removal was successful
Sometimes, after successfully removing a page from the index, you may find that the page still exists within search results and the cache.
To check whether it has been removed, enter the exact URL into the search bar and see what results are returned.
The removal request is case-sensitive, so you will need to submit multiple versions of the URL if your URLs do not redirect to their lower-case versions and if canonicalization is not present.
PRO TIP:
It is considered an SEO best practice to ensure all pages redirect to their lower case version because search engines recognize URLs with different cases as being different pages.
4) Ensure you have followed Google’s Removal Guidelines
Remember that the link removal request that you’ve submitted through Google Search Console is not permanent. After 90 days your content could return to search results pages if you haven’t performed the following actions to block access to your content:
- Block URLs with robots.txt
- Block URLs by password-protecting your server directories
- Block search indexing with meta tags
- Opt-out of display on Google+ Local and other Google Properties
With all that in place, you should be good to go!
PRO TIP:
Blocking URLs with robots.txt only tells search engines not to crawl that page but it may still appear in search results. The best way to remove content is by deleting the page entirely. If you do this, be sure to set up an appropriate 301 Redirect as we mentioned at the beginning of this article. That or add a no-index tag to the page with a canonical reference to the appropriate/original page.
Still having problems?
Google does not provide phone support for these kinds of issues; however, you can connect with other individuals that may have had similar issues to yourself on the Google Product forums.
If that doesn’t work for you and your business is struggling with how Google is indexing your content, don’t hesitate to call us or submit a question through our website. We’d be happy to help!
This blog was originally published on December 10, 2015 but was updated in February of 2020.